Explainer: Understanding the Nasal Septum and Its Role in Breathing
Dr. Poonam Singla
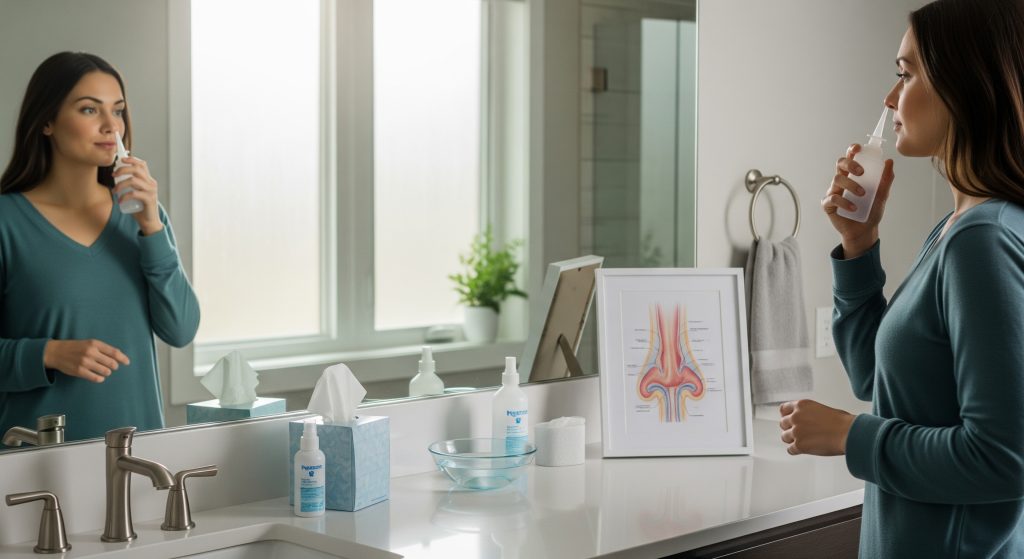
Breathing problems are often blamed on allergies or colds. The quieter culprit is frequently the Nasal Septum. If you understand how this thin midline partition shapes airflow, you can judge symptoms more accurately and decide when treatment is worth it. This explainer sets out the essentials. It is basically a practical guide to how the Nasal Septum works, how it goes wrong, and how you restore efficient nasal breathing.
Core Functions and Structure of the Nasal Septum
Anatomical Components: Cartilage, Bone, and Mucosa
Your Nasal Septum is a composite structure with cartilage at the front and bone at the back.
Blood Supply and Nerve Distribution
The Nasal Septum receives a rich blood supply, especially at the front. As StatPearls observes, Kiesselbach’s plexus in the anterior septum is a common source of nosebleeds.What this means: minor trauma can feel dramatic. Heavy vascularity and sensitive innervation magnify symptoms, though the underlying injury may be small.
Primary Functions in Nasal Breathing
The Nasal Septum divides the cavity and guides laminar airflow. As StatPearls notes, the nasal passages condition air by warming, humidifying, and filtering it, while ciliary action clears debris towards the throat. You sense the effect most in cold weather when mouth breathing feels raw but nasal breathing feels comfortable.
-
Air direction: the septal surface helps organise flow against the turbinates.
-
Resistance balance: small changes in septal shape alter perceived effort.
-
Structural support: the septal L-strut preserves dorsal and tip stability.
Role in Humidifying and Filtering Air
Efficient air conditioning depends on surface area, mucus quality, and controlled airflow. As StatPearls explains, columnar epithelium and mucous cells trap particles, while the turbinates increase contact time for warming and humidification. The Nasal Septum keeps the corridor stable so those processes stay consistent.
The mucociliary escalator does the cleanup. Air arrives cooler, drier, and dirty. It should reach the throat warmer, wetter, and cleaner. That is the job.
Impact on Sinus Drainage Patterns
Sinus health depends on open pathways at the osteomeatal complex. As NCBI describes, blockage here changes pressure and encourages mucosal thickening. If the Nasal Septum buckles towards the middle meatus, drainage can stall.
Evidence links septal deviation with sinus disease. As StatPearls notes, a deviated Nasal Septum can redirect mucociliary transport and raise airway resistance.Practical takeaway: if recurrent sinusitis clusters on one side, assess the Nasal Septum and the osteomeatal complex together. One problem often feeds the other.
Deviated Nasal Septum: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Congenital vs Acquired Deviations
A deviated nasal septum may be present from birth or acquired later. In practice, childhood knocks, sports injuries, or prior surgery can all shift the Nasal Septum. Small angles produce subtle symptoms. Larger angles can distort the nasal valve and increase resistance significantly.
Common Symptoms and Breathing Difficulties
Symptoms scale with the degree and location of bend. As Mayo Clinic outlines, you may experience one-sided blockage, headaches, facial pressure, or reduced smell. Night-time snoring and mouth breathing often worsen during colds and allergy seasons.
Nasal obstruction also links with sleep-disordered breathing. As PubMed reports, obstruction raises the risk of apnoeic events. That does not make a deviated septum the only cause.
Physical Examination and Diagnostic Techniques
Assessment begins with history and anterior rhinoscopy. Nasal endoscopy adds detail and clarifies contact points. CT imaging helps when sinus disease or intricate deformities are suspected.
Classification of Septal Deviations
|
Pattern |
Typical impact |
|
Vertical spur |
Local contact, headache, epistaxis risk |
|
C-shaped bend |
One-sided blockage and turbulent flow |
|
S-shaped bend |
Alternating obstruction and valve collapse |
When Medical Intervention Becomes Necessary
Intervene when symptoms persist despite medical therapy, or when complications develop. As Narrative Review notes, significant obstruction affects smell, headaches, rhinosinusitis, and sleep apnoea. Septoplasty is effective in restoring function with high satisfaction and low complication rates.
Treatment Options for Septal Conditions
Conservative Management Approaches
Conservative measures reduce mucosal swelling around a crooked Nasal Septum. As Mayo Clinic outlines, options include nasal corticosteroid sprays, decongestants, and saline irrigation. Allergy control with antihistamines helps if triggers are prominent, as AENT Associates notes.
For septal injuries or fractures, initial care focuses on bleeding control and preventing septal haematoma. As StatPearls explains, observation may suffice in mild cases, while severe deviations affecting airflow may need surgery later.
-
Daily isotonic saline rinses for hygiene and crust reduction.
-
Topical steroids for mucosal inflammation.
-
Short courses of decongestants for acute flares only.
Septoplasty Surgery: Techniques and Procedures
Septoplasty surgery straightens the Nasal Septum and preserves support.Endoscopic septoplasty offers excellent visualisation and can reduce complications compared with open methods, as PubMed indicates.
Turbinate management is often paired to avoid residual obstruction
Recovery Process and Post-Operative Care
Recovery aims to protect the corrected Nasal Septum, control swelling, and maintain cleanliness. As Mayo Clinic advises, you should avoid strenuous activity early, elevate your head during sleep, and follow precise nasal care instructions. Many resume routine activity within one to two weeks.
Saline care speeds symptom resolution. A small trial found a 58% symptom reduction by day seven with hypertonic seawater solutions, as PubMed reported. Be mindful of risks. Septal perforation and crusting can occur, so review is essential, as StatPearls notes.
-
Do not blow your nose early after surgery.
-
Avoid NSAIDs if your surgeon advises, and follow pain protocols.
-
Use saline irrigations as directed to reduce crust formation.
One final detail. Small habits like sneezing with your mouth open during week one protect the repair. Simple, but effective.
Managing Nasal Septum Perforations
Nasal septum perforation varies in cause and severity. As StatPearls notes, trauma, autoimmune disease, and iatrogenic injury are common causes. Symptoms include crusting, whistling, bleeding, and dryness. Management ranges from humidification and emollients to prosthetic buttons and surgery.
Mechanical closure helps many patients. Silicone buttons relieve epistaxis and obstruction for suitable perforations.
Success Rates and Long-Term Outcomes
Outcomes depend on baseline anatomy, technique, and adjunct procedures. At 12 months, roughly 60% of patients rate septoplasty outcomes as satisfactory, with meaningful obstruction relief, as PubMed reports.
Frequently Asked Questions
How common is a deviated nasal septum in the general population?
Prevalence estimates vary by methodology, but a deviated nasal septum is very common. Roughly speaking, a majority show some deviation on examination or imaging. Only a subset develop symptoms that justify treatment. The Nasal Septum tolerates mild asymmetry well.
What are the main differences between septoplasty and rhinoplasty procedures?
Septoplasty corrects internal structure to improve airflow by straightening the Nasal Septum. Rhinoplasty changes external shape for form and sometimes function. Combined septorhinoplasty addresses both. In ENT shorthand, septoplasty restores the corridor, rhinoplasty reshapes the facade.
Can a deviated septum correct itself without surgery?
In adults, spontaneous straightening is unlikely. Swelling can fluctuate, so symptoms may wax and wane with medical therapy. Structure persists. When blockage remains despite optimal care, septoplasty surgery becomes a reasonable option.
What causes nasal septum perforation after surgery?
Nasal septum perforation after surgery can follow mucosal injury on both sides, infection, haematoma, or compromised blood supply. Smoking and aggressive postoperative manipulation may increase risk. Good technique and careful aftercare reduce the likelihood.
How long does recovery from septoplasty surgery typically take?
Most people resume routine activities within one to two weeks. Residual swelling and sensitivity settle over several weeks. Depending on the source, full mucosal normalisation may take longer. The Nasal Septum benefits from diligent saline care during this period.
Are there age restrictions for septoplasty surgery?
There is no absolute age cut-off. Surgeons usually defer elective septoplasty until facial growth is near complete. In younger patients with severe obstruction, carefully planned intervention may proceed for health reasons. Suitability depends on anatomy, symptoms, and risk profile.








 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...



