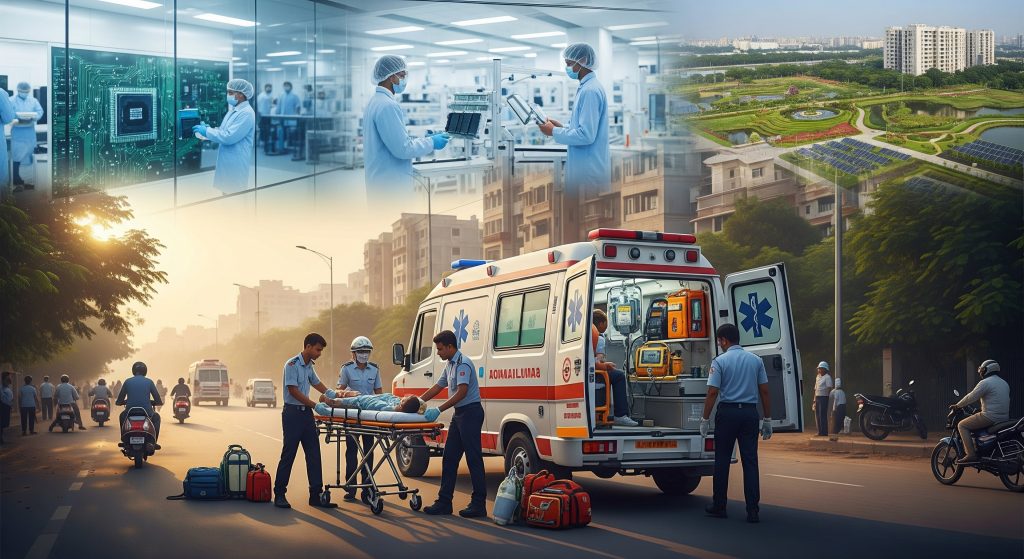
What Is EMS? Meaning, Full Form, and Career Scope in India
Dr. Rajesh Kumar Mishra
EMS is commonly assumed to mean ambulances and flashing lights. That view is too narrow. I address what is ems with precision, because the term spans healthcare, technology, sustainability, and business systems. Understanding EMS meaning across these areas clarifies careers, certifications, and how organisations operate. It also helps avoid costly misalignment when choosing a qualification or a job track.
Types of EMS and Their Meanings
Emergency Medical Services (Healthcare)
When I am asked what is ems in healthcare, I define it as the system that delivers urgent medical care before and during transport to definitive treatment. It covers the 108 call centre, dispatch, ambulances, paramedics, EMTs, and hospital handover protocols. As WHO sets out, prehospital systems require standards for training, resource allocation, and on-scene operations to be effective.
In practice, EMS coordinates multiple moving parts. A two-person crew stabilises an injured patient, communicates a structured handover, and activates the trauma team on arrival. Air ambulances extend that reach when distance matters, and protocols for triage and resuscitation guide priorities. The core idea is simple. Early, appropriate intervention saves lives.
-
Scope: call triage, on-scene care, transport, hospital handover.
-
Roles: EMT, advanced EMT, paramedic, emergency medical officer.
-
Settings: road ambulances, air ambulances, emergency departments.
Here is why this matters for careers. If someone asks what is ems as a profession, it is a structured pathway with clear levels of responsibility. Progression depends on both clinical skill and judgement developed under pressure.
Electronics Manufacturing Services (Technology)
In technology, EMS stands for contract-based electronics manufacturing services. If the question is what is ems in this context, it refers to providers that design for manufacturability, source components, assemble printed circuit boards, and handle testing and logistics. I see EMS full form here tied to end-to-end production support for OEMs.
-
Core offerings: PCB assembly, box build, testing, procurement, and after-sales repair.
-
Customers: consumer electronics, automotive, telecom, and medical device firms.
-
Capabilities: surface mount lines, quality systems, supply chain risk management.
What this means for jobseekers is straightforward. Careers in this EMS track are manufacturing and supply chain focused, not clinical. The EMS meaning shifts with the industry, so the skill sets are distinct.
Environmental Management System (Sustainability)
For sustainability, what is ems becomes an Environmental Management System that structures how organisations plan, implement, check, and improve environmental performance. In a widely used framework, ISO 14001 offers a plan-do-check-act cycle aligned with strategy. As ISO outlines for its 14001:2026 update, the standard strengthens links between environmental management, climate considerations, and resource efficiency.
An EMS in this sense sets policy, defines objectives, tracks legal compliance, and embeds continuous improvement. It is basically how a company moves from ad hoc actions to measurable impact.
-
Elements: policy, aspect-impact assessment, objectives, controls, audits, management review.
-
Outcomes: reduced waste, better compliance, lower risk, and cost control.
-
Careers: EHS officer, sustainability analyst, auditor, environmental manager.
If a colleague asks what is ems for sustainability, I point to the operating system for environmental performance. It is the scaffolding, not a single tool.
Enterprise Management System (Business)
In business, EMS may be used informally to describe an Enterprise Management System that connects planning, operations, and performance. If someone presses on what is ems in this business sense, I explain it as the integrated layer that ties ERP, CRM, and analytics together so leadership can align goals with execution.
-
Functions: strategy cascade, planning cycles, financial and operational dashboards, workflow orchestration.
-
Technology: ERP as the transactional core, CRM for revenue, BI for insight, and integration middleware.
-
Governance: data standards, process ownership, change control.
It is not a single product. It is a coherent approach to run an enterprise without silos (and without duplicate spreadsheets multiplying in the background). The EMS meaning therefore combines process and platform.
Emergency Medical Services Career Opportunities in India
1. EMT-Basic Level Positions
At the foundational level, EMT-Basic roles deliver immediate care under protocols. When students ask what is ems as a first job, this is where I start. The work demands sound assessment, safe transport, and reliable documentation.
-
Typical responsibilities: scene safety, vital signs, CPR, splinting, oxygen therapy, and patient handover.
-
Workplaces: public ambulance networks, private EMS providers, emergency departments.
-
Shift pattern: 8 to 12 hours, rotating nights and weekends in most services.
Training programmes in India blend classroom, skills labs, and clinical postings. Some institutes run two-year diplomas with internships to ensure pre-hospital exposure. I am often asked what is ems certification at this level. It is a competency-based credential confirming readiness for front-line calls.
2. Paramedic and Advanced EMT Roles
Advanced EMTs and paramedics perform invasive procedures and lead on-scene care. When colleagues probe what is ems beyond basic life support, I emphasise clinical judgment under uncertainty. They interpret ECGs, administer drugs under medical direction, and coordinate with receiving hospitals.
-
Advanced skills: IV access, airway adjuncts, rhythm recognition, analgesia under protocol.
-
Leadership: crew resource management, scene command, and clinical decision support.
-
Pathways: advanced diplomas, bridge courses, and supervised practice hours.
I also stress the communication load. Radio reports must be concise, structured, and actionable. One misread detail can set a trauma bay on the wrong footing. That is the difference experience makes.
3. Pre-Hospital Care Specialist
This title often denotes seasoned practitioners who shape protocols, audit cases, and mentor crews. If the question is what is ems expertise at scale, this role embodies it. The remit crosses clinical governance and training.
-
Scope: protocol development, quality assurance, case reviews, and skills refreshers.
-
Impact: reduces variation in care and shortens time to critical interventions.
-
Fit: suited to clinicians who like systems thinking as much as on-scene work.
A practical example helps. A specialist might audit cardiac arrest cases, detect delays in defibrillation, and redesign the kit layout. Small change, large effect.
4. Disaster Management Specialist
Disaster roles sit at the intersection of public health, logistics, and incident command. When I frame what is ems for disasters, I describe planning that holds even when communications fail and when resources are scarce.
-
Responsibilities: hazard assessment, mass-casualty planning, drills, and inter-agency coordination.
-
Training: incident command system, chemical incident management, and medical triage for surge.
-
Employers: state health departments, NDMA-linked projects, large hospital networks.
The skills are broad and pragmatic. Map likely threats, pre-stage supplies, run table-top exercises, and refine after-action reviews. And yet, it is also human work. Communities must trust the plan before they will follow it.
5. EMS Educator and Trainer
Educators translate field practice into teachable modules. When teams ask what is ems education in real terms, I point to scenario design, skills competency checklists, and respectful debriefs. Good training closes the gap between protocols and behaviour.
-
Core tasks: curriculum mapping to competencies, simulation, assessment design.
-
Outcomes: improved on-scene consistency and fewer preventable errors.
-
Profile: experienced clinicians with a talent for communication and feedback.
It is basically quality improvement in a classroom. With high stakes.
6. Medical Officer with EMS Specialisation
Medical Officers in emergency departments or ambulance services oversee clinical governance, supervise crews, and refine pathways of care. If a physician asks what is ems from a medical perspective, I position it as acute care leadership across settings.
-
Clinical scope: triage oversight, protocol authoring, audit leadership, and inter-facility transfer decisions.
-
Teamwork: coordinates with trauma, cardiology, paediatrics, and anaesthesia.
-
Career arcs: emergency medicine core training plus targeted pre-hospital modules.
The best Medical Officers combine clear protocols with practical flexibility. They set standards and still read the room when cases defy the script.
EMS Certification Pathways and Training Requirements
Certificate Courses in Emergency Medical Services
Certificates provide focused, short-duration preparation for entry roles. When candidates ask what is ems certification quickest to start, these programmes are the answer. They emphasise primary survey, CPR, bleeding control, airway basics, and safe transport.
-
Eligibility: typically 10+2, English proficiency, and basic physical fitness.
-
Assessment: skills stations, OSCE-style checklists, and short written tests.
-
Outcome: job readiness for EMT-B roles in ambulance and ER settings.
For those testing the field, a certificate helps validate interest and aptitude before committing to longer programmes.
Diploma and Undergraduate EMT Programmes
Diploma and undergraduate pathways deepen the scope. When families ask what is ems training that builds a career, I recommend diplomas with robust clinical postings. Programmes add pharmacology basics, ECG recognition, trauma simulations, and supervised ambulance rotations.
-
Structure: sequential modules from basic assessment to advanced protocols.
-
Clinical hours: placements across ambulance, ER, ICU, and operation theatres.
-
Progression: eligibility for advanced EMT roles and educator tracks.
The difference shows up on scene. Graduates manage airway, breathing, and circulation in the right order, and they communicate clearly under pressure.
Postgraduate Diploma in Emergency Medical Services
Postgraduate diplomas serve graduates in allied health or medicine seeking leadership roles. When professionals ask what is ems beyond field practice, I describe this as the bridge to governance and system design.
-
Emphasis: protocol development, quality assurance, research literacy, and health systems.
-
Capstone: audits or improvement projects mapping delays to targeted fixes.
-
Outcome: readiness for Pre-Hospital Care Specialist or educator positions.
It is the step from individual competence to system impact.
American Heart Association Certifications
Internationally recognised short courses remain essential. When colleagues ask what is ems certification that employers expect, I list BLS, ACLS, and PALS. These courses refine core algorithms and shared language across teams.
-
BLS: high-quality CPR and AED use for adults, children, and infants.
-
ACLS: advanced cardiac algorithms, airway management, and team dynamics.
-
PALS: paediatric assessment triangle, shock recognition, and dosing.
I advise refreshing these on schedule. Skills drift without deliberate practice.
NSDC Recognition and Government Accreditation
National Skill Development Corporation alignment signals industry relevance. When institutions ask what is ems accreditation that builds trust, I point to NSDC recognition and relevant state health approvals. Public ambulance services often prioritise such credentials in tenders and hiring.
-
Benefits: standardised curricula, employability support, and quality benchmarks.
-
Verification: cross-check institute approvals and placement track records.
-
Funding: some schemes subsidise fees for eligible learners.
Accreditation does not guarantee excellence. It does set a floor that weeds out weak programmes.
Duration and Fee Structure for Different Levels
Timelines vary. Short certificates may run a few months, while diplomas often span multiple semesters with clinical postings. Postgraduate programmes typically add an intensive term for projects or audits. Fees scale with duration, simulation facilities, and clinical access.
|
Programme |
Typical Structure |
|---|---|
|
Certificate (EMT-B) |
Focused modules plus skills labs and an ambulance or ER posting |
|
Diploma / Undergraduate EMT |
Multi-semester coursework with rotations across emergency settings |
|
Postgraduate Diploma (EMS) |
Advanced topics, governance, and an improvement capstone |
When applicants ask what is ems course value at each tier, I advise matching scope to career intent. Do not over-buy training you will not use in the first three years.
Salary Expectations and Career Growth in EMS
Entry-Level EMT Salary Packages
Entry packages are modest but stable, with benefits improving inside large hospital networks and metro-based providers. New EMTs can expect variable allowances for night shifts and high-call zones. Growth is faster where call volumes and training support are high.
-
Drivers of pay: city tier, provider type, and shift complexity.
-
Ways to improve: add BLS and ACLS, keep case logs, and seek high-acuity postings.
-
Trajectory: steady increments with pathway to advanced EMT roles.
For clarity, what is ems growth early on is largely certification-driven. Skills plus documented cases change the conversation at appraisal time.
Experienced Paramedic Compensation
Experienced paramedics command stronger packages due to advanced scope and leadership on scene. Compensation rises with airway proficiency, ECG interpretation, drug administration competencies, and mentoring responsibilities. Premiums are typical for industrial sites and remote projects.
In practice, the best boost is demonstrable outcomes. Reduced scene times, cleaner handovers, and positive audits carry weight.
Medical Officer EMS Specialist Earnings
Medical Officers with EMS focus typically sit higher on the pay ladder, reflecting clinical oversight and governance duties. Compensation aligns with hospital scale, trauma centre designation, and on-call intensity. Roles that design protocols and lead audits tend to attract better packages.
The sustained signal across employers is consistent. Clear clinical leadership and reliable systems thinking earn trust and pay.
Electronics Manufacturing Services Salaries
For electronics manufacturing, salary structures reflect industrial operations more than clinical ladders. Production engineers, test engineers, and supply chain roles map to manufacturing pay scales. Compensation varies with plant location, product complexity, and shift systems.
-
Early career: technician and line-engineer roles with defined skill ladders.
-
Mid career: process engineering, quality, NPI, and vendor management.
-
Senior: plant leadership, programme management, and key account ownership.
If the query is what is ems pay in tech versus healthcare, the determinants differ. Production throughput and yield matter more on the tech side, acuity and clinical scope on the healthcare side.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Progression is tangible with structured upskilling. EMTs move to advanced EMT, then paramedic, then educator or pre-hospital specialist tracks. Physicians grow into Medical Officer roles, then system leadership. A parallel pathway exists into disaster preparedness and command.
-
Levers: targeted certifications, case audits, and mentorship roles.
-
Pivots: from field care to education, quality, or system design.
-
Crossovers: industrial EMS, remote site medicine, and aeromedical teams.
A simple heuristic helps. If the question is what is ems career planning in practice, the answer is skills plus evidence plus visibility.
Regional Salary Variations Across India
Regional differences are material. Metropolitan centres usually offer higher pay and busier caseloads. Tier 2 cities may trade lower packages for broader responsibilities and quicker seniority. Remote assignments often add hardship benefits, which can close the gap.
Cost of living and training availability also shape real take-home value. A slightly lower figure with stronger training can still be the better choice.
Key takeaway: Match training and role to the specific EMS meaning in view. Healthcare EMS, electronics manufacturing, environmental management, and enterprise management reward very different skill sets.
Conclusion
EMS is not a single field. It is a set of domains that share an acronym and little else. If the starting question is what is ems, the precise answer depends on context: clinical care, contract manufacturing, sustainability management, or enterprise operations. Careers in Emergency Medical Services are structured, impactful, and skills-driven. Certifications open doors, audits build credibility, and clean handovers earn trust. For those drawn to systems and measurable results, it is a satisfying path. Choose the track deliberately and build depth, not just credentials.
Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifications are required to become an EMT in India?
Most EMT-B programmes require 10+2, English proficiency, and medical fitness. Some prefer science at school level. Employers prioritise accredited training, current BLS, and clean background checks. If the question remains what is ems eligibility beyond basics, providers often add driving competence and shift readiness.
How long does it take to complete EMS certification?
Short certificates can finish within months, while diplomas span multiple semesters with postings. Postgraduate diplomas usually add an intensive term for projects. The right answer to what is ems duration depends on prior education and target role.
Is EMS certification valid internationally?
Local EMT credentials may not port directly. However, BLS, ACLS, and PALS are widely recognised. For mobility, verify destination country requirements in advance. When asked what is ems portability, I advise mapping competencies to that regulator’s scope list.
What is the difference between EMT and paramedic roles?
EMTs provide basic life support under protocol. Paramedics add invasive procedures, drug administration, and on-scene leadership. If clarity is needed on what is ems tiering, think scope of practice plus clinical judgement.
Can I pursue EMS courses after completing 12th standard?
Yes. Many certificate and diploma programmes accept 10+2 graduates. Stronger science foundations help but are not always mandatory. The practical question is what is ems path that aligns with career goals and budget.
What are the job prospects for EMS professionals in 2026?
Prospects remain favourable in urban centres and organised networks. Growth is likely where training quality, dispatch systems, and hospital integration are improving. As far as current data suggests, emergency care demand continues to rise with urbanisation.








 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...



