Cardiac MRI Explained: What You Need to Know
Dr. Hriday Kumar Chopra
Disclaimer: The content shared here is for informational purposes only. Always consult a specialist doctor before attempting any treatment, procedure, or taking any medication independently. Treatment costs and pricing may vary depending on the patient’s condition, medical requirements, hospital, and other factors.
Old advice still suggests a basic echo can answer every heart question. It cannot. When tissue characterisation, subtle scarring, or precise function matter, I rely on Cardiac MRI. It shows structure, function, and blood flow in one sitting. No radiation. Just high fidelity data that changes decisions. In this explainer, I outline what the scan detects, the full cardiac MRI procedure, when contrast is essential, key limitations, and the practicalities in India.
What Cardiac MRI Detects and Diagnoses
Heart Structure and Function Assessment
I use Cardiac MRI when I need a definitive assessment of chamber size, wall motion, and tissue signals. The technique acquires cine sequences across multiple planes, so I see the heart working in real time. It is basically a moving blueprint. Tissue characterisation sequences help separate oedema, fat, scar, and fibrosis. That level of clarity supports diagnosis and management, especially where echocardiography leaves unanswered questions.
In practice, this means I can quantify ventricular volumes, mass, and ejection fraction with high reproducibility. That consistency matters for heart failure follow up. Mapping techniques such as T1 and T2 add detail on diffuse fibrosis or inflammation. When a patient presents with suspected myocarditis, the signal patterns across these maps guide therapy. Precision beats guesswork.
-
Quantifies left and right ventricular volumes and ejection fraction with tight error margins.
-
Identifies focal scar and diffuse fibrosis using parametric mapping and late enhancement.
-
Assesses pericardial thickness and constrictive physiology with dynamic imaging.
-
Evaluates blood flow direction and velocity for shunts and valvular jets.
One example helps. A young athlete with atypical chest pain and a normal echo still showed subepicardial enhancement on Cardiac MRI. That pattern pointed to prior myocarditis, not coronary disease. Different diagnosis. Different plan.
Coronary Artery Disease Detection
Cardiac MRI can assess coronary disease indirectly and, in selected settings, directly. Stress perfusion imaging reveals subendocardial ischaemia at rest or under vasodilator stress. Wall motion under stress gives a functional readout of supply demand mismatch. Late gadolinium enhancement identifies infarcted segments and differentiates acute from chronic injury with typical patterns. It is not a replacement for coronary CT angiography, but it adds tissue truth. And yet, when revascularisation is on the table, tissue viability from Cardiac MRI is decisive.
-
Stress perfusion detects flow limitation before wall motion changes.
-
Viability assessment distinguishes stunned or hibernating myocardium from non-viable scar.
-
Oedema imaging helps stage infarction in the acute period.
Cardiomyopathy Evaluation
For cardiomyopathies, Cardiac MRI is my reference standard for phenotype and prognosis. I can distinguish dilated, hypertrophic, arrhythmogenic, and restrictive patterns by combining function and tissue signatures. Late gadolinium enhancement shows scar distribution, which correlates with arrhythmic risk in several subtypes. T1 mapping supports detection of diffuse processes such as amyloidosis or early hypertrophy. Here is why that matters. Treatment often hinges on the specific pattern, not just on the ejection fraction.
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: asymmetric hypertrophy with patchy midwall or RV insertion enhancement.
-
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: right ventricular dilation, wall motion abnormalities, and fibrofatty change.
-
Restrictive or infiltrative disease: elevated native T1 and extracellular volume with distinct enhancement patterns.
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy: chamber dilation, global hypokinesis, and midwall septal enhancement in many cases.
This is specialist territory, but a quick note on jargon. I often refer to LGE, which means late gadolinium enhancement. It is the pattern of contrast retained in scarred myocardium. It is basically the scar map.
Heart Valve Problems
Cardiac MRI quantifies regurgitant volumes and fractions with phase contrast sequences. That helps when Doppler windows are limited or when multivalvular disease complicates echo grading. I also assess aortic root dimensions and flow eccentricity in bicuspid aortic valve disease. For complex repairs, preoperative data on flow jets and ventricular response add value. Precision is practical here, not academic.
-
Direct measurement of aortic and pulmonary regurgitant fraction.
-
Assessment of mitral and tricuspid regurgitation severity when echo is indeterminate.
-
Visualisation of prosthetic valve motion without acoustic shadowing.
Congenital Heart Disease
In adults with congenital heart disease, a heart mri scan provides geometry, shunt quantification, and right ventricular metrics in one examination. That breadth is helpful in repaired tetralogy, complex shunts, and post-arterial switch follow up. Serial scans chart right ventricular volumes and function with consistency. Surgical planning benefits, and so does surveillance during adulthood.
Post-Heart Attack Damage Assessment
Cardiac MRI maps infarct size, microvascular obstruction, and haemorrhage after an acute event. Those findings have prognostic weight. Infarct transmurality also predicts functional recovery after revascularisation. I use that information to tailor medication and rehabilitation. Rehabilitation plans change when the jeopardised area is small or when stunning is likely to recover.
Cardiac Tumours and Masses
Characterising masses requires signal behaviour across sequences and contrast phases. Cardiac MRI differentiates thrombus from tumour in most cases. It also suggests benign versus malignant features using perfusion and tissue signals. When surgical decisions carry risk, that differentiation prevents unnecessary intervention.
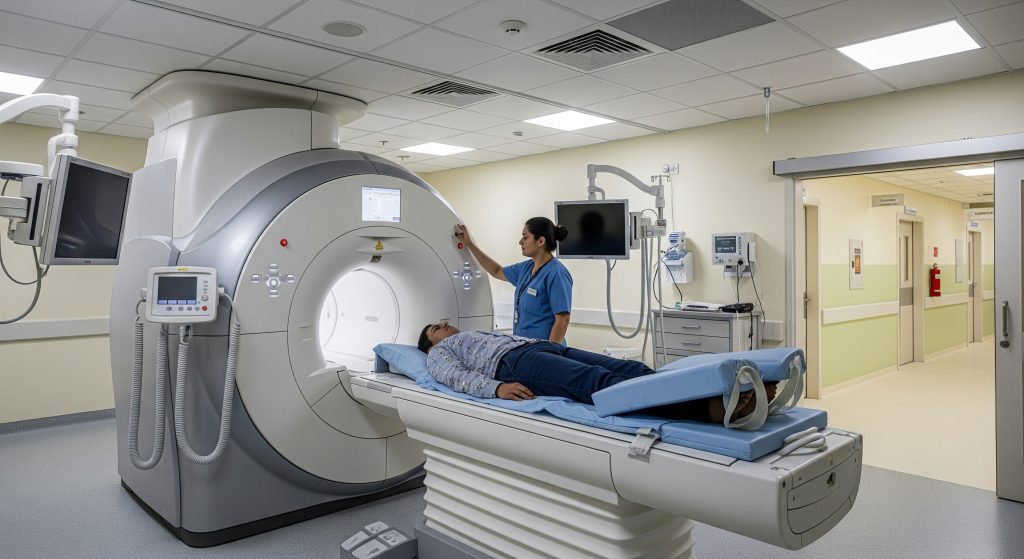
Complete Cardiac MRI Procedure
Pre-Scan Preparation Requirements
I advise comfortable clothing without metal, and I review implant cards beforehand. Some patients require blood tests to check kidney function, especially if contrast is planned. Caffeine should be avoided on the day if stress perfusion is scheduled. Nitrates or beta blockers may be paused depending on the protocol, but only after clinician review. Safety screening is non-negotiable.
-
Bring previous imaging and reports for reference.
-
Remove jewellery, watches, and contactless cards.
-
Discuss anxiety, claustrophobia, or breathing difficulties in advance.
Step-by-Step Scanning Process
-
Safety screening and consent. I review implants, allergies, and recent procedures.
-
ECG leads are placed, and a coil is positioned over the chest.
-
Localiser images are acquired to plan cardiac planes.
-
Cine imaging captures chamber motion across short and long axes.
-
Flow sequences evaluate vessels or valves as needed.
-
If indicated, I proceed with cardiac mri with contrast for perfusion and scar imaging.
-
Post-processing includes volumetric and flow quantification.
The environment is loud due to gradients. Ear protection is provided. Communication with the team continues throughout via intercom and squeeze bulb.
Contrast Agent Administration
I use gadolinium-based contrast when perfusion or scar imaging is required. A small intravenous cannula is placed before the scan. The dose is calculated by weight and delivered via power injector for consistency. Patients often note a brief cool sensation in the arm. Most can continue the exam comfortably.
-
Perfusion first pass during stress and rest, if indicated.
-
Late enhancement typically acquired 8 to 15 minutes after injection.
Breath-Holding Techniques
Clear images depend on steady breath holds. Each breath hold usually lasts 8 to 12 seconds. I coach the rhythm through the intercom so the timing is predictable. If breath holds are difficult, I adjust sequences or use motion correction. The aim is usable images, not a perfect performance. Perfect is rare and unnecessary.
ECG-Gating and Heart Monitoring
ECG-gating synchronises imaging to the cardiac cycle. That allows accurate frame assignment for systole and diastole. I monitor rhythm throughout and adapt if ectopy is present. In arrhythmias, real-time sequences can rescue image quality to an extent. Data integrity comes first.
Duration and Positioning
Most studies take between 30 and 60 minutes, depending on sequences. Complex protocols can take longer. Patients lie supine with the head outside or inside the bore based on scanner length. Padding supports the back and arms to reduce motion. Small adjustments improve comfort and image quality.
Cardiac MRI with Contrast
Gadolinium Contrast Agent Safety
Modern macrocyclic gadolinium agents have a favourable safety profile in patients with normal renal function. Allergic reactions are uncommon and usually mild. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis risk is very low with current agents when kidney function is adequate. I check renal function if there is any concern. Caution is sensible, panic is not.
When Contrast is Necessary
I reserve contrast for clinical questions that require perfusion or scar assessment. Suspected ischaemia, viability before revascularisation, myocarditis evaluation, and most cardiomyopathies benefit. When the question is pure function, non-contrast cine imaging may suffice. The protocol should match the clinical decision being considered.
Late Gadolinium Enhancement Applications
Late gadolinium enhancement highlights scar and fibrosis with striking clarity. Infarction appears subendocardial or transmural in coronary territories. Non-ischaemic fibrosis shows midwall or subepicardial patterns. In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, patchy enhancement informs risk stratification to a degree. For myocarditis, a subepicardial lateral wall pattern is common. Pattern recognition is not a parlour trick. It guides prognosis and therapy.
Perfusion Imaging Benefits
Stress perfusion detects ischaemia before resting wall motion changes. It supports decisions on further testing or intervention. Combined with viability imaging, it answers the two key questions. Is there flow limitation. Will the myocardium recover. That combination prevents unnecessary procedures and missed opportunities alike.
Risks and Contraindications
-
Severe renal impairment may preclude gadolinium use, depending on agent and risk.
-
Unstable arrhythmias can limit image quality and may require alternative strategies.
-
Implant incompatibility remains a hard stop in some cases.
-
Severe claustrophobia may necessitate sedation or an open scanner.
These are manageable risks with proper screening and planning. The benefit often outweighs the constraints, though not without exceptions.
Important Considerations and Limitations
Safety with Pacemakers and Implants
Many modern pacemakers and defibrillators are MRI-conditional. I confirm model, leads, and conditionality, then coordinate device programming. Monitoring during and after scanning is standard. For non-conditional devices, risk rises, and scanning is usually avoided or restricted to highly specialised centres. Metal fragments and some cerebral aneurysm clips remain absolute contraindications. Safety is procedural, not theoretical.
Pregnancy Considerations
Non-contrast Cardiac MRI may be performed during pregnancy when clinically justified. First trimester imaging is often deferred unless urgent. Gadolinium crosses the placenta and is generally avoided unless benefit clearly outweighs risk. I discuss timing and alternatives with the obstetric and cardiology teams. Prudence serves everyone.
Claustrophobia Management
Claustrophobia can derail an otherwise straightforward study. I plan ahead. A detailed walkthrough, reassurance, mirror glasses, or music often helps. Short bore scanners reduce the enclosed feeling. For severe anxiety, I consider anxiolytics with appropriate supervision. The goal is cooperation and comfort without compromising safety.
Kidney Function Requirements
For contrast studies, I check recent eGFR where risk factors exist. If renal function is reduced, I weigh the incremental value of contrast against risk. Non-contrast imaging remains powerful for many indications. Where contrast is essential, I choose the safest agent and dose. It is a measured decision, not a blanket rule.
Cost Factors in India
Cost varies by city, facility type, and the need for contrast. As BookMerilab notes, typical charges range from ₹9,500 to ₹14,000, with machine type and protocol influencing price. In some centres, entry pricing is lower. As LabsAdvisor reports, the starting figure is roughly ₹9,025 in select locations. Specific packages can also be advertised at fixed rates. As HOD advertises, a cardiac mri with contrast may be listed at around ₹9,499 with pre-test requirements clearly stated.
Two practical tips apply. First, ask whether the quote includes contrast and reporting. Second, confirm if stress perfusion or advanced mapping incurs extra fees. Insurance coverage for diagnostics varies by policy, and pre-authorisation may be required. Upfront confirmation prevents surprises.
Comparing with Other Heart Imaging Tests
|
Test |
Best Use |
Strengths |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cardiac MRI |
Tissue characterisation, function, viability |
No radiation, comprehensive data, high reproducibility |
Availability, scan time, implant restrictions |
|
Echocardiography |
First line function and valves |
Widely available, bedside, dynamic haemodynamics |
Limited windows, less precise volumes, tissue limits |
|
Coronary CT Angiography |
Coronary anatomy and plaque |
High negative predictive value, fast |
Radiation, contrast iodine, limited tissue character |
|
Nuclear Perfusion |
Perfusion and ischaemia burden |
Well validated, widely used |
Radiation, lower spatial resolution |
|
Invasive Angiography |
Therapy and precise anatomy |
Intervention ready, pressure data |
Invasive risks, no tissue information |
There is no single winner. The right study answers the clinical question at hand. Cardiac MRI complements other modalities and often clarifies uncertain findings. Maybe that is the point. Choose the test that changes the decision, not the one that merely adds images.
Making Informed Decisions About Cardiac MRI
Decision making starts with the question to be answered. If the aim is precise function, valve quantification, and tissue character, Cardiac MRI is often superior. If coronary anatomy is the central issue, coronary CT may be faster and more direct. I align the choice with the clinical fork in the road. Does the result affect medication, device therapy, or a procedure. If not, I reconsider the test.
-
Match modality to decision. Anatomy, function, perfusion, or scar.
-
Confirm safety and implant compatibility early.
-
Discuss breath holds and comfort strategies in advance.
-
Clarify costs and inclusions, especially contrast and stress testing.
For many patients, a single heart mri scan answers multiple questions. That efficiency helps avoid serial testing and conflicting results. And yet, multimodality care remains essential in complex disease. Use Cardiac MRI for what it does best, and add other tools when they add decisions, not noise.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a cardiac MRI scan take?
Most scans take 30 to 60 minutes. Add time if stress perfusion or extensive mapping is required. The timeline includes safety checks, positioning, and contrast phases when used. I plan for short breaks between sequences if needed. Comfort supports quality.
Is cardiac MRI safe for people with heart implants?
Many MRI-conditional pacemakers and defibrillators can be scanned under a strict protocol. I confirm model and leads, coordinate programming, and monitor throughout. If a device is not MRI-conditional, scanning may be unsafe outside a specialised centre. The device team should be involved from the start.
What is the cost of cardiac MRI in major Indian cities?
Prices vary by facility and protocol. Expect a range from about ₹9,000 to ₹14,000 in many centres, with stress or contrast typically higher. Check whether reporting, contrast, and any stress agent fees are included. Package pricing can simplify budgeting.
Can children undergo cardiac MRI?
Yes, paediatric protocols exist, and Cardiac MRI is valuable in congenital heart disease. Younger children may need sedation for stillness and breath holds. A paediatric team should review safety and dosing for contrast use. Preparation and child-friendly coaching improve success.
How often should cardiac MRI be repeated?
Repeat timing depends on the condition and the decision to be made. For stable cardiomyopathy, annual or biennial scans may suffice. After intervention, a tailored interval is chosen to document recovery or progression. Unnecessary repetition adds little value. Decisions matter more than dates.
What should I avoid before a heart MRI scan?
Avoid metal objects and clothing with metallic fibres. Skip caffeine on the day if stress perfusion is planned. Discuss medications such as nitrates or beta blockers with the clinician in advance. Arrive early to complete safety screening without rush. Preparation improves outcomes.
Summary for quick action
-
Use Cardiac MRI when tissue detail, precise function, or viability will drive a decision.
-
Confirm implants, kidney function, and potential need for contrast early.
-
Prepare for short breath holds; raise claustrophobia concerns beforehand.
-
In India, expect a quoted range near ₹9,000 to ₹14,000 depending on protocol and centre.







 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...








