RRT Medical Abbreviation Explained with Examples
Dr. Deepak Jain
Advice to treat the rrt medical abbreviation as a single meaning is risky. Context drives everything. In clinical notes, a handover, or a family update, RRT can point to an emergency team, a kidney support therapy, or a credentialed clinician. I explain how to read it accurately, how to act on it, and where ambiguity creeps in. The goal is simple. Fewer misunderstandings and faster, safer care when the stakes are high.
Common Meanings of RRT in Medicine
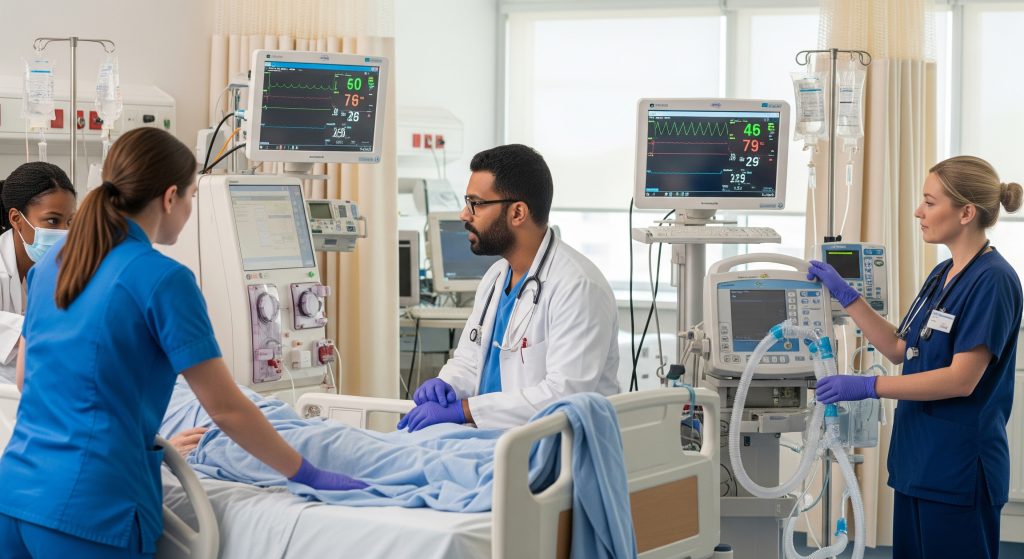
1. Rapid Response Team (Emergency Medical Team)
In many hospitals, the rrt medical abbreviation most often refers to a rapid response team. It is a mobile, expert group that arrives at the bedside when a patient shows signs of acute deterioration. I view it as a safety net that catches patients before they fall into full crisis. Some hospitals report better survival and shorter stays following team activation, while others show mixed outcomes. That variation reflects how teams are staffed, trained, and triggered. It also reflects case mix and timing. Good systems save minutes. Minutes often save lives.
-
Typical triggers include sudden hypoxia, hypotension, altered consciousness, and staff concern.
-
Core tasks cover assessment, stabilisation, and decisions on transfer or escalation.
-
Documentation closes the loop and informs the primary team’s next steps.
When someone writes rrt in a ward message about decompensation, this meaning is almost certain. But location still matters. I return to that judgment later.
2. Renal Replacement Therapy (Kidney Treatment)
In nephrology notes, the rrt medical abbreviation usually means renal replacement therapy. The phrase covers haemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, continuous renal replacement therapy, and kidney transplantation. I use rrt medical abbreviation here to remind teams that the patient may be on a chronic regimen or an acute rescue modality. The difference shapes staffing, monitoring, and discharge planning.
-
Haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis remove solutes and fluid to maintain homeostasis.
-
Continuous renal replacement therapy supports unstable ICU patients with gentle fluid shifts.
-
Transplantation offers definitive renal replacement for selected candidates.
When a handover says, “Start RRT tonight,” it rarely means a committee. It means dialysis or CRRT, and urgency is implied.
3. Registered Respiratory Therapist (Healthcare Professional)
In respiratory care, rrt medical abbreviation can designate a Registered Respiratory Therapist. This is a professional credential that signals advanced competence in ventilator management, airway care, and cardiopulmonary assessment. Candidates must pass two examinations to hold the credential, and as National Board for Respiratory Care states, those are the Therapist Multiple-Choice and the Clinical Simulation Examinations. In theatre, ICU, and emergency settings, an RRT may lead ventilator weaning, troubleshoot gas exchange issues, and train ward teams on equipment. Expertise at the bedside reduces errors and delays. It also improves confidence across the team.
Rapid Response Team Explained
Team Composition and Structure
A mature rapid response team blends acute care skills with calm bedside leadership. I typically expect a critical care nurse, a respiratory therapist, and physician backup. Some centres deploy an ICU registrar as the primary clinician. Others use senior nurses with standing orders and direct lines to on-call doctors. The structure matters less than clarity. Who leads the assessment. Who calls for extra help. Who documents and hands over.
-
Core members: critical care nurse, respiratory therapist, and a medical officer on call.
-
Clear authority: the team must escalate, transfer, or initiate therapies without delay.
-
Feedback loop: case reviews and debriefs strengthen the system and training.
I advise a simple rule for the rrt medical abbreviation in staffing rosters. Spell out Rapid Response Team the first time. Then use RRT consistently.
Activation Criteria and Protocols
Activation criteria should be standardised and visible at the point of care. They must also allow clinical judgement. Abnormal vital signs, rising oxygen needs, new confusion, chest pain, or staff concern should all count. As PubMed Central reports, abnormal vitals can signal deterioration up to 6 to 8 hours before a serious adverse event. Early calls buy time. Time creates options.
-
Recognise the trigger. Use NEWS2 or equivalent, and allow staff worry as a valid reason.
-
Call the team. Give location, brief history, and immediate hazards.
-
Stabilise the patient. Airway, breathing, circulation, disability, exposure. Keep it structured.
-
Decide disposition. Remain in place with a plan, step up to HDU, or transfer to ICU.
-
Document and hand over. State diagnosis, actions, medications, and the watch plan.
Hospitals differ in thresholds and call pathways. That heterogeneity affects impact to an extent. The safe principle holds. Make it simple to call early and hard to ignore a warning score.
Examples of RRT Interventions
The rrt medical abbreviation often appears in event logs for short, decisive actions. A few representative scenarios clarify how the team works in practice.
-
Severe hyperkalaemia: administer insulin with dextrose, nebulised salbutamol, calcium for membrane stabilisation, and arrange urgent dialysis if needed.
-
Acute hypoxia on the ward: optimise positioning, apply high flow oxygen or initiate CPAP, draw gas, and escalate to ICU if persistent.
-
Septic shock concern: activate sepsis bundle, start broad spectrum antibiotics after cultures, give fluid boluses, and start vasopressors per protocol.
-
New stroke symptoms: stroke call, time of onset confirmed, rapid imaging, and thrombolysis or thrombectomy pathway without delay.
Each example underlines a pattern. Stabilise fast and hand over a clear plan.
Renal Replacement Therapy Detailed
1. Hemodialysis
Haemodialysis is the workhorse modality behind the rrt medical abbreviation in nephrology contexts. It filters blood through a dialyser to remove toxins and excess fluid when kidneys fail. Preparation usually involves creating vascular access, such as an arteriovenous fistula. Sessions run on a strict schedule, with medication and diet aligned to the regimen. For acute kidney injury, haemodialysis may be a bridge. For chronic kidney disease, it can be a long-term lifeline.
-
Venue: in-centre units or supervised home setups.
-
Focus: control of uraemia, potassium, acid base status, and volume.
-
Teamwork: nephrology, nursing, dietetics, and pharmacy all coordinate.
When notes state, “Start RRT,” and the patient is haemodynamically stable on a ward, haemodialysis is often intended. The rrt medical abbreviation here points to a machine, not a team.
2. Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneum as a semi permeable membrane. Dialysate flows in through a catheter, sits to exchange solutes, and then drains. I consider PD when vascular access is difficult, when lifestyle flexibility is a priority, or when gentle fluid shifts are safer. In acute kidney injury, PD can support unstable patients with gradual clearance. It can also be set up quickly in resource limited settings.
-
Advantages: independence, haemodynamic stability, and fewer rapid fluid shifts.
-
Trade offs: risk of peritonitis, catheter care burden, and protein losses.
-
Use cases: AKI with poor access, chronic therapy at home, and bridging to transplant.
When a chart uses the rrt medical abbreviation on a surgical ward with a PD catheter noted, PD is the likely interpretation.
3. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Continuous renal replacement therapy supports critically ill, unstable patients over 24 hours. It removes fluid and solutes gently, which helps when rapid shifts would worsen shock. Modalities vary by the method of clearance and filter setup. In practice, the ICU, nephrology, and nursing teams run CRRT together. They adjust dose, anticoagulation, and fluid balance hour by hour. The rrt medical abbreviation in ICU often points to this continuous therapy.
-
Indications: volume overload with shock, severe acidosis, refractory hyperkalaemia, and overt uraemic complications.
-
Modalities: continuous venovenous haemofiltration, haemodialysis, and haemodiafiltration.
-
Risks: filter clotting, electrolyte shifts, and line complications.
CRRT is not a destination. It buys stability while the underlying illness is treated.
4. Kidney Transplantation
Transplantation replaces renal function with a donor kidney. It changes the goals of care from clearance to graft protection and long term survival. Immunosuppression, infection surveillance, and cardiovascular risk management become central. When discharge paperwork says, “RRT discontinued post transplant,” the rrt medical abbreviation marks a milestone. It signals a new phase of care, not a modality choice.
Indications for Starting RRT
Clinicians often ask for a simple list. Reality is nuanced, but the standard triggers hold. I group the renal replacement therapy indications into urgent, relative, and trajectory based categories. The rrt medical abbreviation in this context will mean therapy, not team or credential.
|
Trigger |
Practical explanation |
|---|---|
|
Refractory hyperkalaemia |
Medical therapy cannot control potassium safely. |
|
Severe metabolic acidosis |
pH low despite bicarbonate and cause control. |
|
Pulmonary oedema with hypoxia |
Diuretics failing and ventilatory support is threatened. |
|
Uraemic complications |
Encephalopathy, pericarditis, or bleeding risk emerges. |
|
Intoxications |
Dialysable toxins where clearance changes outcomes. |
|
Ongoing oliguria with rising urea |
Trajectory shows worsening despite optimised care. |
Two notes matter. First, context decides urgency. Second, earlier initiation makes sense if a clear trend points to harm. It is a clinical judgement call, though algorithms help.
Examples of RRT Applications
Examples make the rrt medical abbreviation concrete for teams.
-
AKI in septic shock: CRRT runs to remove fluid gently while vasopressors are titrated.
-
Chronic haemodialysis patient with missed sessions: urgent dialysis for volume and potassium control.
-
Toxic alcohol ingestion: haemodialysis as an adjunct to antidotes for rapid clearance.
-
Bridging to transplant: maintenance dialysis while evaluation and matching proceed.
Earlier, I highlighted the three CRRT modalities. That matters when matching solute targets to the patient. Clearance goals differ and so do risks.
Context-Based Identification
Clinical Setting Clues
Setting usually solves the rrt medical abbreviation puzzle in seconds. In a medical ward during an urgent call, RRT means rapid response team. In ICU with an unstable AKI patient, RRT points to continuous renal replacement therapy. In theatre notes about ventilator strategy, RRT likely marks the Registered Respiratory Therapist in attendance.
-
Location: ward emergency vs dialysis unit vs ICU vs operating theatre.
-
Time: overnight pager alerts often involve a team call. Daytime rounds often involve therapy planning.
-
Equipment: mention of dialyser, filter, or access lines indicates therapy rather than a team.
Use the full phrase once in high risk handovers. Then use the abbreviation. It keeps the record precise and efficient.
Documentation and Charting
A small discipline avoids large confusion. I recommend a first mention rule in notes and discharge letters. Write the term in full followed by the abbreviation in brackets. For example, Rapid Response Team (RRT) or Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT). Then keep usage consistent. Avoid switching meanings in a single document. The rrt medical abbreviation must never do double duty on the same page.
-
First use in full with abbreviation in brackets.
-
Define again if the care context changes within the same admission.
-
Avoid mixed meanings in orders and medication charts.
This approach seems simple. It prevents near misses more often than it gets credit for.
Communication Tips for Healthcare Teams
Verbal communication carries extra risk under time pressure. I apply three habits to reduce ambiguity when the rrt medical abbreviation is spoken aloud.
-
Say the full term on first mention during an urgent call or huddle.
-
State the goal explicitly, such as “initiate dialysis now” or “activate the rapid response team.”
-
Close the loop by asking the receiver to repeat the action and timing.
In quiet settings, write and read back. In noisy settings, confirm the patient, location, and intent. It sounds basic. It is the backbone of safe care.
Conclusion
The rrt medical abbreviation carries three common meanings that sit in different parts of hospital life. Rapid Response Team. Renal Replacement Therapy. Registered Respiratory Therapist. Correct interpretation depends on setting, timing, and the surrounding details. Use the full term once in documentation. Keep usage consistent. When stakes rise, remove the guesswork by stating the action and the target clearly. Clarity saves time and, to an extent, it saves outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common meaning of RRT in hospitals?
On general wards during urgent calls, the rrt medical abbreviation most often means the rapid response team. In nephrology notes and ICU charts, it more often means renal replacement therapy. The correct reading depends on location and context.
When should a Rapid Response Team be activated?
Activate for abnormal vital signs, sudden hypoxia, new confusion, severe pain with instability, or when staff feel uneasy about a patient. As PubMed Central highlights, abnormal vitals can precede serious deterioration by 6 to 8 hours. Early calls are safer than late ones.
What are the main types of renal replacement therapy?
Haemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, continuous renal replacement therapy, and kidney transplantation. The rrt medical abbreviation in renal contexts points to one of these modalities. Choice rests on stability, access, solute targets, and patient preference.
How does CRRT differ from regular dialysis?
CRRT runs continuously with gentle fluid and solute removal. It suits haemodynamically unstable ICU patients. Intermittent haemodialysis runs for set sessions and removes fluid faster. The rrt medical abbreviation in ICU discussions usually signals CRRT when shock is present.
Can RRT mean different things in different hospital departments?
Yes. That is the practical challenge. On a ward emergency call, RRT means rapid response team. In renal clinics, it means renal replacement therapy. In respiratory care rosters, it can mean Registered Respiratory Therapist. The rrt medical abbreviation must be defined on first use.
What qualifications does a Registered Respiratory Therapist need?
RRT credential holders complete the required education and pass two examinations. As National Board for Respiratory Care notes, these are the Therapist Multiple-Choice and Clinical Simulation Examinations. The credential signals advanced competency in respiratory care.
How long does renal replacement therapy typically last?
Duration varies. In acute kidney injury, therapy can be short term until renal recovery. In end stage kidney disease, dialysis is ongoing unless a transplant is performed. The rrt medical abbreviation in plans should include the expected course and review points.
rrt medical abbreviation rrt medical abbreviation rrt medical abbreviation rrt medical abbreviation rrt medical abbreviation








 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...








