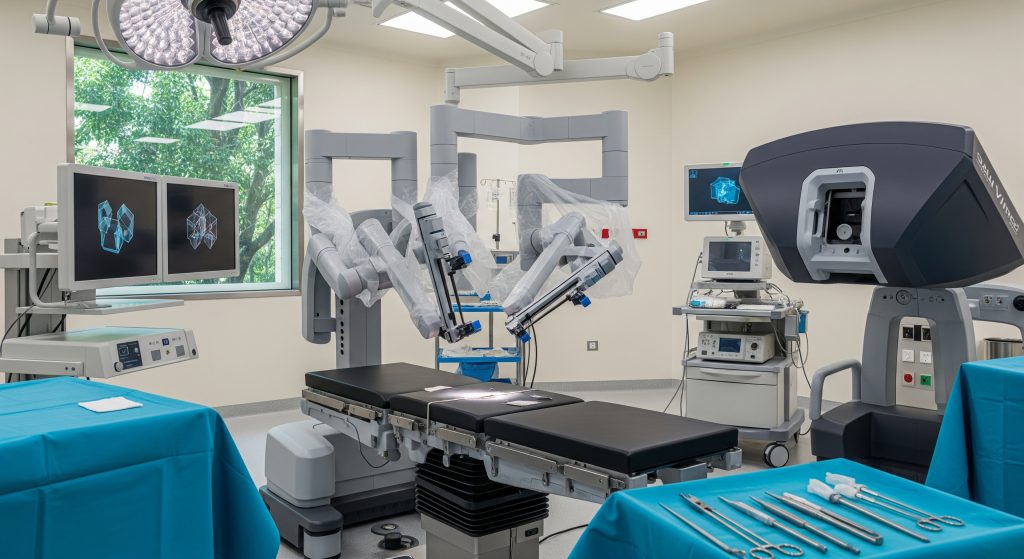
Overview of the Da Vinci Surgical System and Its Benefits
Dr. Shiv Chopra
Robots supposedly replace surgeons. That claim misses the point. The da vinci surgical system is a precision tool that extends human judgement. It translates refined hand movements into stable, micro-accurate actions. It gives vision where access is difficult. And it helps maintain consistency when fatigue would normally creep in. In practice, the value is simple. Better access, controlled motion, and fewer trade-offs during complex procedures.
Current Models and Capabilities of Da Vinci Systems
Da Vinci 5: Force Feedback Technology and Advanced Features
I regard the latest platform as an inflection point. The da vinci surgical system in its fifth generation adds meaningful haptics at the console. Surgeons sense pressure through Force Feedback, which supports gentler tissue handling during delicate dissection. Console ergonomics are improved, and workflow tools now reduce friction between steps.
Two practical gains matter in theatre. First, real-time cues on instrument force guide safer traction. Second, event review allows the team to replay a moment without stopping the case. As Intuitive reports, the platform incorporates over 150 innovations, including Force Feedback that helps reduce applied force on tissue. That number signals breadth, not just a new colour scheme.
-
Enhanced imaging and stable 3D vision improve depth judgement in confined fields.
-
Smart commands accelerate routine actions, which trims micro-delays between tasks.
-
Built-in analytics support continuous skill development across cases.
There is still nuance. Early experience suggests comparable perioperative outcomes to established systems. The learning curve for experienced console surgeons appears minimal, yet longer term datasets will settle the debate. I would still position this da vinci surgical system as a practical upgrade when soft-tissue finesse is critical.
Da Vinci Xi: Multi-Port System with 3D Visualisation
The Xi remains the workhorse. This da vinci surgical system uses a multi-port setup with long-reach arms and overhead architecture. That design helps with multi-quadrant access. It is especially useful for colorectal, upper GI, and complex pelvic work where angles change mid-case.
Optics are strong. Surgeons operate in immersive 3D HD with motion scaling and tremor filtration, which increases precision during fine suturing. On accuracy, the system demonstrated submillimetric average error in test tasks, as PMC notes, which supports reliable image-guided manoeuvres. In the pit, this yields cleaner geometry for stapling, dissection, and knot tying.
-
Multi-arm control from the console allows stable retraction and exposure.
-
Port placement flexibility streamlines access across abdominal quadrants.
-
Built-in tremor filtration aids delicate work near critical structures.
Critics point to cost and set-up time. Fair. But training standardisation and smoother docking have reduced overhead to an extent. The argument now is about value delivered per minute in complex cases.
Da Vinci SP: Single-Port System for Narrow Surgical Spaces
The SP is different. This da vinci surgical system works through a single port. Three instruments and a scope articulate within a confined corridor. It shines in narrow spaces such as the oropharynx or deep pelvis where traditional triangulation is not feasible.
In transoral robotic surgery, the platform offers tight bends and stable visualisation through one incision. That translates into fewer external incisions and controlled instrument choreography. Urological and head and neck teams have leveraged this to approach complex anatomy without spreading access points.
-
Single incision reduces external trauma and simplifies wound care.
-
Articulated instruments regain triangulation internally.
-
Console control preserves precision despite constrained working envelopes.
SP is not a universal solution. It is a focused tool for specific indications where a narrow entry path is non-negotiable. The gain is elegant access when space is the main constraint.
Da Vinci X: Entry-Level Platform for Robotic Programmes
For hospitals building capacity, the X offers a sensible on-ramp. This da vinci surgical system shares many core components with higher tiers. It retains 3D vision, articulated instruments, and motion scaling. It therefore supports safe adoption for high-volume procedures.
Two attributes make it attractive. First, modularity. Upgrades can extend capability as a programme matures. Second, cost efficiency relative to the Xi while keeping key features for complex soft-tissue work. For patients, the promise stands: fewer and smaller incisions, stable control, and thoughtful ergonomics that reduce surgeon fatigue.
-
High-definition 3D view enhances depth and suture placement.
-
Console motion scaling converts broad hand moves into fine instrument action.
-
Responsive arms maintain range in tight anatomy without excessive torque.
For leadership teams, I advise a staged rollout. Begin with a defined case list and clear metrics. Expand only once safety and efficiency targets are consistently met.
Key Benefits and Advantages for Patients
Smaller Incisions and Reduced Scarring
Patients see the result on day one. The da vinci surgical system enables smaller port sizes and fewer large incisions. Tissue planes are respected, and retraction is more controlled. Scars are typically shorter and less conspicuous. This is not cosmetic only. Smaller access correlates with gentler postoperative recovery and fewer wound issues.
-
Shorter skin incisions mean less disruption to muscle and fascia.
-
Precision dissection reduces collateral tissue trauma around the target site.
-
Lower tension on closure improves scar quality in suitable patients.
Roughly speaking, this is the core of minimally invasive surgery. Less disruption for the same operative goal.
Shorter Hospital Stays and Faster Recovery Times
Length of stay is a hard outcome that patients care about. The da vinci surgical system supports less invasive access, which commonly reduces LOS across routine indications. In a multi-procedure analysis, robot-assisted approaches showed lower median hospital LOS compared with open or laparoscopic techniques, as PubMed reports. That aligns with what teams observe on the ward.
-
Earlier mobilisation due to reduced pain and smaller wounds.
-
Lower transfusion rates allow faster rehabilitation and fewer delays.
-
Streamlined discharge thanks to predictable postoperative courses.
Recovery time hinges on more than technique. ERAS pathways (a structured protocol for perioperative care) tighten the loop further. Combine a da vinci surgical system with ERAS, and the gains tend to compound.
Less Blood Loss and Pain Management
Stability reduces bleeding. The da vinci surgical system allows precise energy application and measured traction. That lowers microvascular injury during dissection. Less blood loss often translates into fewer transfusions and cleaner postoperative courses.
Pain is similar. Smaller incisions and controlled instrument paths change the analgesic profile. I favour multimodal regimens that pair regional blocks with non-opioid foundations. Patients typically mobilise earlier and need fewer rescue doses.
-
Targeted local anaesthetic at port sites reduces immediate postoperative pain.
-
Scheduled non-opioids limit nausea and sedation that slow mobilisation.
-
Clear home protocols cut readmissions for uncontrolled discomfort.
The net effect is practical. Fewer drains, fewer side effects, and a steadier recovery curve. It is basically good surgical housekeeping powered by stable instrumentation.
Lower Risk of Complications and Infections
Complications cluster when access is large and control is inconsistent. The da vinci surgical system helps by stabilising exposure and reducing contact surfaces. Smaller incisions lower wound infection risk. Precision reduces inadvertent serosal or vascular injury. Conversion to open surgery becomes less common in suitable cases.
-
Reduced exposure of deep tissue to ambient contamination.
-
Consistent pneumoperitoneum supports haemostasis and visibility.
-
Fine instrument control reduces energy spread to adjacent structures.
And yet, no platform eliminates risk. Patient selection, surgeon skill, and perioperative protocols remain decisive. Technology amplifies good processes. It does not replace them.
Enhanced Precision Through Tremor Filtration
Every surgeon has micro tremor. The da vinci surgical system filters that noise and scales motion. Subtle wrist rotations become steady instrument tips. In microscale tasks, this matters. Ureteral anastomosis, intracorporeal suturing, and delicate lymphadenectomy benefit from stability.
-
Motion scaling converts larger hand movements into smaller instrument motions.
-
Tremor filtration dampens oscillation for fine control near critical anatomy.
-
Stable 3D visualisation preserves depth perception during precise tasks.
Precision translates into fewer unintended tissue events and more reliable sutures. Not always spectacular. Just consistently better.
Clinical Applications Across Medical Specialties
1. Urological Procedures and Prostate Surgery
Urology adopted robotics early for good reasons. The da vinci surgical system excels in the deep pelvis, where access is narrow and nerves matter. Radical prostatectomy is the emblematic case. Stable exposure, magnified vision, and measured traction help preserve continence and erectile function where possible.
-
Partial nephrectomy benefits from precise tumour excision and renorrhaphy.
-
Pyeloplasty gains from stable suturing in confined spaces.
-
Cystectomy and urinary diversions leverage consistent intracorporeal reconstruction.
Outcomes still depend on surgeon experience. Volume and careful technique remain the edge.
2. Gynaecological Surgery and Hysterectomy
For complex hysterectomy and endometriosis, the da vinci surgical system offers controlled dissection with less traction on fragile tissue. Enhanced vision clarifies planes around the ureter and uterine vessels. In practice, patients often experience reduced blood loss and quicker return to function.
-
Myomectomy with layered closure benefits from motion scaling for deep sutures.
-
Endometriosis resection requires careful work around bowel and bladder.
-
Pelvic organ prolapse repairs rely on steady mesh fixation and knot security.
Costs can be competitive in experienced units. When theatre time and LOS fall, the total pathway begins to balance nicely.
3. General Surgery and Gastrointestinal Procedures
In upper GI and colorectal surgery, exposure quality drives outcomes. The da vinci surgical system provides stable retraction and durable visualisation for foregut, bariatric, and colorectal resections. Intracorporeal anastomosis becomes more consistent, which can simplify extraction site decisions.
-
Cholecystectomy is straightforward, but complex cases benefit from articulation.
-
Hiatal hernia repair uses precise crural suturing in a tight mediastinum.
-
Right colectomy with intracorporeal anastomosis reduces midline incision length.
The theme is controlled geometry. Clean angles for staplers. Predictable needle paths. Fewer compromises when the field gets crowded.
4. Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery Applications
For thoracic lobectomy and mediastinal work, the da vinci surgical system enables fine manoeuvres around vessels and airways. Stable 3D vision and tremor filtration support precise dissection near critical structures. In cardiac settings, selected valve repairs through mini-access benefit from articulated instruments and consistent exposure.
-
Internal mammary harvest and pericardial access can be highly controlled.
-
Thoracic lymphadenectomy sees clearer planes with measured traction.
-
Robotic mitral repair uses steady suturing in a limited space.
Patient satisfaction improves when pain and LOS are lower. That said, careful selection and specialised training are non-negotiable here.
5. Colorectal and Hepatobiliary Operations
Deep pelvic resections test any platform. The da vinci surgical system helps maintain clean mesorectal planes and stable ties near autonomic nerves. For liver work, articulation aids posterior segments where angles frustrate straight instruments. Biliary reconstruction benefits from magnified suturing with stable exposure.
-
Total mesorectal excision with precise nerve preservation aims to reduce dysfunction.
-
Low colorectal anastomoses favour intracorporeal control and gentle handling.
-
Choledochojejunostomy requires reliable needle control and knot security.
These are demanding cases. The platform mitigates technical strain and, to an extent, reduces variability between long cases.
Making Informed Decisions About Da Vinci Surgery
Technology should serve clinical goals. That is the standard I apply. The da vinci surgical system is appropriate when it improves precision, reduces access trauma, or enhances safety for the anatomy in question. It is less useful when exposure is simple, or when cost and time add no countervailing value.
Here is a concise framework I use when advising on approach selection.
|
Decision factor |
What to assess |
|---|---|
|
Patient-specific anatomy |
Narrow spaces, prior surgery, BMI, and vascular variants. |
|
Procedure complexity |
Need for delicate suturing, multi-quadrant access, or re-do surgery. |
|
Team experience |
Console time, complication profile, and mentoring structure. |
|
Pathway efficiency |
Dock-to-cut times, LOS, and ERAS adherence. |
|
Outcome priorities |
Blood loss, pain, function preservation, and recovery speed. |
|
Cost and access |
Per-case cost versus expected reduction in downstream utilisation. |
Questions I recommend asking the surgical team:
-
Why is the da vinci surgical system preferred over laparoscopy for this case?
-
How many of these cases has the console surgeon completed in the past year?
-
What does the unit’s audited complication profile show for this indication?
-
What ERAS elements are used alongside the da vinci surgical system to speed recovery?
-
What are the alternatives, and how do risks differ for my anatomy?
Selecting the approach is not about gadgets. It is about matching controlled access to the anatomy and objectives.
Pros and cons, stated plainly:
-
Pros: Precise motion, stable 3D vision, smaller incisions, and reproducible intracorporeal suturing.
-
Cons: Higher capital costs, longer set-up for new teams, and limited value in straightforward cases.
I keep one more principle. Robotic-assisted surgery is a method, not a badge. The da vinci surgical system should win on clinical merit and pathway value. Nothing else.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical cost of Da Vinci surgery in India?
Costs vary by city, hospital tier, and case complexity. The da vinci surgical system adds equipment charges and consumables. In practice, bundled packages often include anaesthesia, theatre, and stay. I advise comparing total pathway costs, not list prices. Consider LOS, transfusions, and readmissions when judging value.
Does insurance cover Da Vinci surgical procedures?
Many insurers cover medically necessary procedures regardless of approach. The da vinci surgical system is the technique, not the indication. Coverage depends on policy terms, hospital empanelment, and pre-authorisation rules. Ask the insurer to confirm eligibility and any co-pay linked to robotic-assisted surgery specifically.
How long does recovery take after Da Vinci surgery?
Recovery depends on the operation and baseline health. With the da vinci surgical system, discharge often occurs earlier than with open surgery. Return to desk work might take 1 to 2 weeks for minor procedures. Demanding activity takes longer. ERAS compliance and home support shape the timeline significantly.
Which hospitals in India offer Da Vinci surgical systems?
Availability is concentrated in tertiary centres and high-volume private hospitals. The da vinci surgical system is expanding to regional hubs as programmes mature. Focus less on the building and more on the team’s audited outcomes for your procedure.
Can all surgeons perform Da Vinci procedures?
No. Surgeons require specific console training, proctoring, and case volume to maintain proficiency. The da vinci surgical system rewards repetition. Ask about the surgeon’s recent case numbers and the team’s complication metrics.
What are the risks associated with robotic surgery?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and anaesthetic complications. The da vinci surgical system also carries platform-specific risks such as instrument failure or docking delays. These are uncommon in experienced units. The principal risk remains the disease itself and the complexity of the operation.
Final thought. Good surgery is disciplined craft and clear judgement. The da vinci surgical system helps when precision, access, and consistency matter most. Choose it for the right cases, with the right team, and with a clear plan for recovery.







 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...








