Leg MRI Scan Explained: Uses, Procedure, and Results
Dr. Neetan Sachdeva
Conventional wisdom says an X-ray or ultrasound will suffice for most leg problems. That shortcut often misses early soft tissue change and subtle bone stress. When decisions carry consequence, I prefer clarity. An mri scan leg offers that clarity with cross-sectional detail that influences treatment on day one.
Common Conditions Diagnosed by Leg MRI Scans
Ligament Injuries (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL)
Ligament injuries present as instability, buckling, or a clear loss of confidence under load. Clinical tests guide suspicion, but an mri scan leg will map fibre disruption, oedema, and associated bone bruising. As Mayo Clinic explains, MRI confirms the diagnosis and excludes concurrent injuries, which matters for surgical planning.
-
ACL and PCL: evaluate fibre continuity, pivot-shift bruising, and meniscocapsular tears.
-
MCL and LCL: grade sprains, avulsion fragments, and periligamentous swelling.
What this means is simple. The right graft choice, or bracing, follows better visualisation. An mri scan leg gives that visualisation when the exam is equivocal.
Meniscal Tears and Cartilage Damage
Patients often describe catching, locking, or joint line pain after a twist. An mri scan leg distinguishes longitudinal from radial tears, detects meniscal root injuries, and shows cartilage delamination that X-ray will miss. I look for extrusion, parameniscal cysts, and marrow oedema that explain symptoms.
-
Menisci: tear pattern and stability risk.
-
Cartilage: depth, location, and subchondral response.
Repair or debridement decisions improve when the tear pattern is unambiguous. That is the practical value of an mri scan leg here.
Muscle Strains and Tendon Ruptures
Clinical grading of strains is helpful, but imaging guides return-to-sport timing. An mri scan leg quantifies fibre disruption, haematoma size, and tendon retraction in partial or full tears. It is basically a roadmap for rehab progression, and for surgery when retraction is significant.
-
Hamstrings and calf: intramuscular vs musculotendinous injuries.
-
Achilles and quadriceps tendons: gap measurement and tissue quality.
Reinjury risk tracks with healing quality. An mri scan leg can show it.
Stress Fractures and Hidden Bone Injuries
Early stress reactions evade plain films for weeks. An mri scan leg detects periosteal oedema, microtrabecular injury, and fracture lines before cortical changes appear. This can shorten the path to offloading and prevent a complete fracture.
-
Tibia and metatarsals: early marrow signal change without visible crack.
-
Femoral neck or shaft: high-risk sites where delays carry consequences.
There is a trade-off in sport. Time lost now preserves the season later. An mri scan leg helps strike that balance.
Joint Disorders and Arthritis
Arthritis is not just cartilage loss. Synovitis, bone marrow lesions, meniscal damage, and effusions drive pain and function. An mri scan leg assesses all four domains in one sitting. As Mayo Clinic outlines, imaging complements examination to stage disease and tailor management.
-
Osteoarthritis: cartilage thinning, osteophytes, and subchondral marrow lesions.
-
Inflammatory arthritides: synovial hypertrophy, erosions, and enthesitis.
Treatment focuses better when the pain generator is defined. An mri scan leg brings that definition into focus.
Soft Tissue Tumours and Infections
Unexplained masses or deep infections demand anatomical precision. An mri scan leg characterises size, margins, necrosis, and involvement of fascia or neurovascular bundles. This shapes biopsy approach and informs urgency. Infections show fluid collections, sinus tracts, and bone involvement that change therapy.
-
Tumours: signal patterns that suggest benign vs aggressive behaviour.
-
Infections: abscess localisation and osteomyelitis assessment.
Staging and planning live or die by anatomical truth. An mri scan leg provides that truth without radiation.
Congenital Abnormalities and Birth Defects
Congenital limb differences are complex, and surgery is best planned with full anatomy in view. An mri scan leg outlines cartilage anlage, dysplastic bones, and soft tissue anomalies that X-ray cannot resolve in young patients. It supports earlier, cleaner intervention and realistic rehabilitation planning.
-
Lower limb shortening patterns and associated joint changes.
-
Ligamentous and muscular variants relevant to stability and gait.
The aim is straightforward. Fewer surprises in theatre, more predictable outcomes. An mri scan leg reduces uncertainty.
Complete Leg MRI Procedure Step-by-Step
Pre-Scan Preparation Requirements
I advise arriving early, wearing metal-free clothing, and bringing previous imaging. An mri scan leg is usually straightforward, but good preparation avoids delays. Eat normally unless sedation is planned. Hydration helps if contrast is likely, and it helps veins.
-
Carry implant cards or device details if relevant.
-
List allergies and kidney conditions for screening.
Preparation does not need to be elaborate. It needs to be precise.
Metal Screening and Safety Protocols
Safety screening is non-negotiable. The magnet is always on. Patients must remove jewellery, piercings, and any ferromagnetic items. Certain devices can be scanned under strict protocols. As RadiologyInfo notes, many pacemakers are now MR-conditional and require coordinated programming and monitoring during an mri scan leg.
-
Disclose surgeries, shrapnel exposure, or metal work in the eyes.
-
Inform the team about pregnancy and breastfeeding for tailored planning.
Claustrophobia is manageable with wide bore systems, coaching, or light sedation. The protocol will be adapted, but the safety checklist remains fixed. An mri scan leg proceeds only when it is safe to proceed.
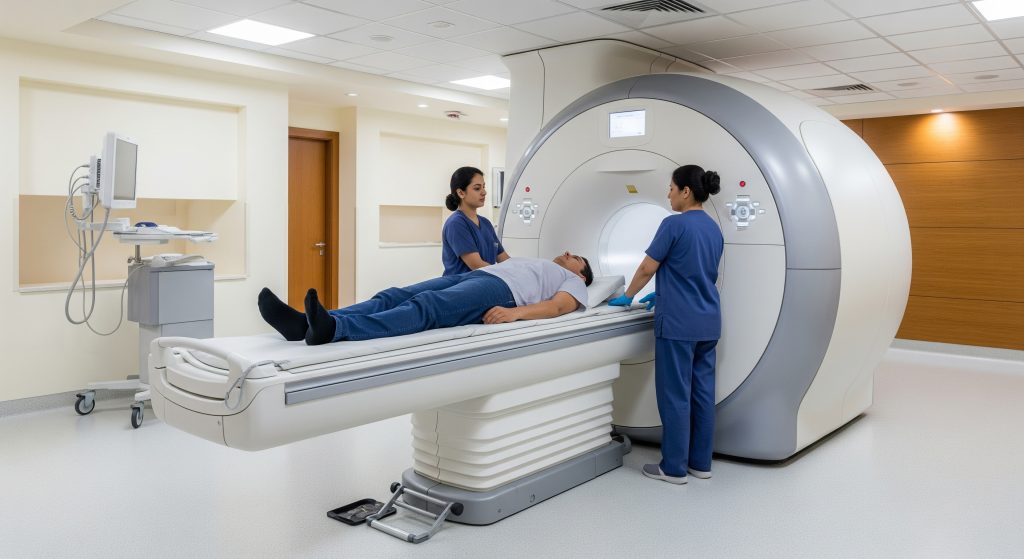
Patient Positioning and Scanner Types
Positioning depends on the target region. For knee and ankle work, a dedicated extremity coil improves signal and detail. For thigh or hip, a body or large array coil is used. An mri scan leg in a wide bore scanner suits larger patients and those with mild claustrophobia.
-
Sponges and straps reduce motion and improve sharpness.
-
Neutral joint positions avoid artefacts and mimic function.
Better positioning equals fewer repeats. Fewer repeats equal faster results.
Contrast Dye Administration Process
Some studies require intravenous contrast. The goal is simple: enhance inflamed tissues, tumours, or complex post operative anatomy. Contrast for an mri scan leg is gadolinium based in most centres. Screening covers allergies and kidney function, as NSF risk rises in severe renal impairment.
-
Consent, cannulation, and dose based on weight and indication.
-
Most reactions are mild and short lived, though monitoring is prudent.
Contrast is not routine for every leg study. It is chosen for the question at hand. That restraint protects patients and improves diagnostic yield.
Duration and What to Expect During Scanning
Patients often ask about time. A standard an mri scan leg typically takes between 30 and 60 minutes depending on sequences and whether contrast is used. As Ganesh Diagnostic explains, expect loud gradients with ear protection provided, and short holds to reduce motion.
-
Remain still to avoid blur and repeat runs.
-
Use the call bell if uncomfortable, and communicate early.
The procedure is painless. The table time pays off in diagnostic confidence. An mri scan leg earns its place with answer quality.
Post-Scan Instructions and Recovery
Most patients resume normal activity immediately. If sedation was used, escort and rest are necessary. After a contrast enhanced an mri scan leg, drink water and report any unusual symptoms. Results are compiled by a radiologist, then sent to the referring clinician for correlation.
-
Keep the cannula site clean if there was contrast.
-
Book a follow up to discuss findings and next steps.
Fast reporting matters when treatment decisions are pending. Set that expectation at booking.
Leg MRI Cost in India
Price Range Across Major Indian Cities
Pricing varies by city, magnet strength, and whether contrast is needed. In Bengaluru, the price for a routine an mri scan leg ranges roughly from ₹3,650 to ₹6,630. As Labsadvisor notes, centre type and promotions influence the final bill.
Large metros often show wider spreads across neighbourhoods and hospital networks. Smaller cities trend lower, though subspecialty protocols can raise costs. I advise comparing inclusions rather than headline price alone.
Government vs Private Hospital Pricing
Government facilities usually offer the lowest tariff, but waiting lists can be significant. Private hospitals charge more, yet often include faster reporting, subspecialty reads, and flexible timing. Diagnostic chains may offer promotions for an mri scan leg while keeping turnaround fast.
-
Public hospitals: lower fees, longer waits, limited appointment slots.
-
Private centres: higher fees, rapid access, broader scheduling.
Price is one factor. Service levels, reporting quality, and access often justify a modest premium.
Factors Affecting MRI Scan Costs
-
Magnet strength: 3T studies can cost more than 1.5T due to higher demand.
-
Protocol length: multiregion or bilateral an mri scan leg increases time and cost.
-
Contrast: adds cannulation, drug cost, and monitoring time.
-
Specialist reporting: musculoskeletal subspecialists may carry a surcharge.
-
Urgency: same day reporting can attract express fees.
-
Location: prime urban centres price higher than peripheral areas.
Understanding these drivers helps negotiate or choose wisely. It also frames realistic expectations before booking an mri scan leg.
Insurance Coverage and Reimbursement
Most comprehensive policies cover medically indicated MRI with a valid referral. Pre authorisation is common for outpatient scans. I recommend confirming network centres, cashless eligibility, and documentation requirements before an mri scan leg.
-
Submit referral, clinical notes, and any prior imaging.
-
Ask about co-pays, caps per study, and exclusions for contrast.
Reimbursement hinges on paperwork quality. Keep all receipts and the final radiology report.
Ways to Reduce Your MRI Expenses
-
Use network providers to access cashless or discounted tariffs.
-
Ask for a non contrast study if clinically reasonable after discussion.
-
Choose a diagnostic chain with bundled pricing for an mri scan leg.
-
Request a standard 1.5T protocol when 3T is not essential to the question.
-
Book during weekday hours when staffing is optimal and prices are stable.
The goal is value, not the absolute lowest number. Pay for accuracy and reliability, and avoid repeat scans.
Making Informed Decisions About Your Leg MRI Scan
Good imaging is a means to an end. The end is a correct diagnosis and a plan that works. Before scheduling an mri scan leg, confirm the clinical question, whether contrast is necessary, and the expected reporting time. During the visit, optimise comfort and stillness. Afterward, close the loop with a timely consultation.
I keep one principle front and centre. Imaging should answer a focused question and change management. When the question is tight, an mri scan leg becomes both efficient and decisive.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a leg MRI scan typically take?
A standard an mri scan leg typically runs for 30 to 60 minutes depending on sequences and contrast. Complex protocols or bilateral studies can extend that window. Arrive early to avoid cascading delays.
Is leg MRI safe during pregnancy?
Non contrast MRI is generally considered safe in pregnancy when clinically justified. For an mri scan leg, teams weigh benefit and timing with obstetric input. Gadolinium contrast is usually avoided unless the diagnostic need is compelling.
What’s the difference between 1.5T and 3T MRI machines?
3T provides higher signal and finer spatial resolution than 1.5T. That can shorten scans or improve detail for an mri scan leg. However, not every indication benefits meaningfully, and artefacts can increase at 3T in some cases.
Can I have an MRI with metal implants in my body?
Many implants today are MR-conditional with strict protocols in place. Before an mri scan leg, the team will review implant type, location, and safety documentation. Some older devices remain contraindicated, so disclosure is essential.
Do I need to fast before a leg MRI scan?
Fasting is not required for a routine an mri scan leg. If sedation is planned, fasting instructions will be provided. Hydration is helpful, especially when contrast is anticipated.
When will I receive my leg MRI results?
Most centres deliver reports within 24 to 72 hours. Urgent studies can be expedited. For an mri scan leg with contrast or complex findings, allow time for subspecialty review if requested.







 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...








