Heart MRI Scan Explained: What to Expect and Why It Matters
Dr. Hriday Kumar Chopra
Disclaimer: The content shared here is for informational purposes only. Always consult a specialist doctor before attempting any treatment, procedure, or taking any medication independently.
Conventional advice says an ultrasound is enough for most heart questions. It often is. But there are times when only a heart MRI scan answers the clinical why and the clinical how. I explain what it shows, how the process unfolds, safety points that matter, and how to decide if it is the right next step.
What a Heart MRI Scan Shows and Detects
1. Coronary Artery Disease Detection
A heart MRI scan assesses how well blood reaches the heart muscle during rest and stress. I look for perfusion defects that suggest flow limitation. When necessary, I combine this with wall motion analysis to see if a territory moves abnormally during stress. That pattern helps distinguish old scarring from active ischaemia. In practice, this is helpful when treadmill tests are indeterminate or when symptoms persist despite normal basic workups.
2. Heart Valve Disorders Assessment
I use a heart MRI scan to quantify regurgitation and stenosis severity when echocardiography leaves doubt. Velocity-encoded sequences measure forward flow and backflow volumes, giving regurgitant fraction and stroke volume. This produces robust numbers that guide timing for intervention. It also shows ventricular size and function, which influence valve surgery decisions.
3. Cardiomyopathy Identification
A heart MRI scan provides high fidelity views of ventricular size, shape, and function, and it characterises tissue. This matters for dilated, hypertrophic, and restrictive patterns. I assess fibrosis or scarring using contrast techniques and mapping. That tissue signature helps differentiate genetic disease from myocarditis or ischaemic injury and can refine prognosis and follow up.
4. Congenital Heart Defects
For congenital lesions, I rely on 3D anatomy, shunt quantification, and precise flow data. A heart MRI scan maps complex connections, measures right and left ventricular volumes, and evaluates repaired pathways. It is particularly useful after childhood surgery when adults present with exercise intolerance. Clear outflow tract views and branch pulmonary artery flow make clinical planning far easier.
5. Heart Muscle Damage Evaluation
When prior infarction is suspected, a heart MRI scan can separate viable from non-viable myocardium. I examine infarct size, location, and the transmural extent of scar. Combined with wall motion and perfusion, this guides revascularisation decisions and device therapy. In suspected myocarditis, the same approach highlights inflammation and oedema patterns that support the diagnosis.
6. Pericardial Disease Detection
Pericardial inflammation alters signal and thickening, both visible on a heart MRI scan. I also assess constrictive physiology by checking ventricular interdependence and diastolic filling patterns. Effusions are easily characterised, and adhesions can be inferred from motion abnormalities. This is particularly useful when echocardiography gives limited views or when clinical signs remain ambiguous.
7. Cardiac Masses and Tumours
When a mass is seen on ultrasound or CT, a heart MRI scan helps define its tissue characteristics and its relationship to nearby structures. I evaluate fat, haemorrhage, cystic components, and vascularity patterns. That profile supports differentiation between thrombus, benign lesions, and malignant processes. It also assists surgical planning by clarifying attachments and invasion risk.
8. Blood Flow and Circulation Analysis
Quantitative flow is a practical strength. A heart MRI scan measures shunt ratios, valve jets, and vessel flow patterns. I use this to assess aortic disease, pulmonary hypertension effects, and post-procedure haemodynamics. When symptoms puzzle the team, precise flow numbers often resolve the uncertainty.
Complete Step-by-Step Cardiac MRI Procedure
Pre-Scan Preparation Requirements
I start with a safety checklist. Devices, implants, and prior reactions to contrast are documented. Caffeine or heavy meals may be restricted before stress sequences. I advise comfortable clothing without metal. For anxious patients, I discuss strategies early. That might include practice breath holds or a mild anxiolytic. Consistency at this stage improves image quality later.
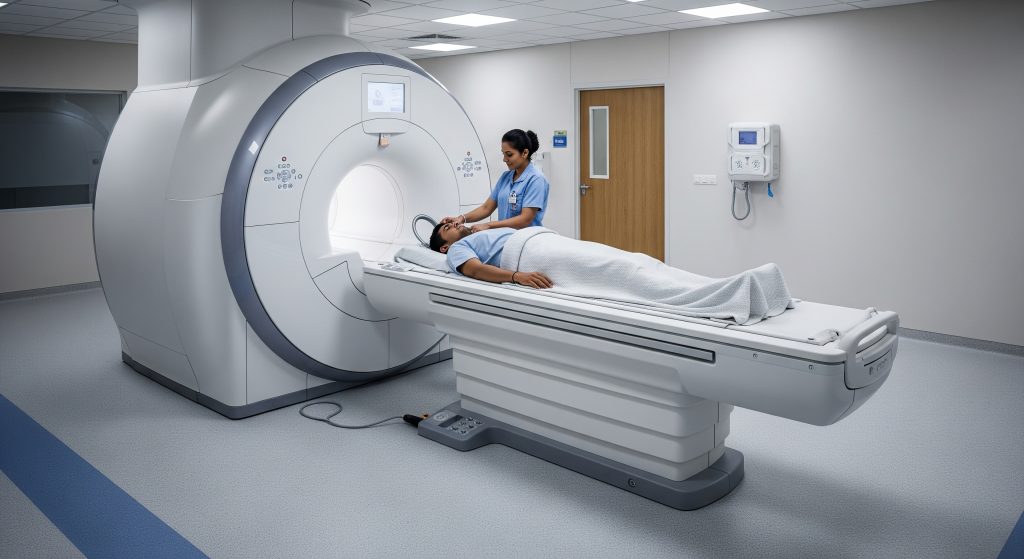
1. Positioning on the MRI Table
Technologists position the patient supine on the table with cardiac coils aligned over the chest. Padding and straps keep the body still. I confirm comfort and alignment, because minor adjustments prevent repeats. Ear protection is provided due to scanner noise.
2. ECG Lead Placement
Three to four leads are placed to synchronise imaging with the heartbeat. Good ECG signal quality is essential. I ask the patient to relax and avoid chest muscle tension, which can cause artefacts. Clear triggering leads to crisp cine images and better measurements.
3. Contrast Injection Process
If contrast is planned, a cannula is placed before entering the scanner. I explain that the agent improves tissue characterisation and perfusion assessment. Injection timing is coordinated with specific sequences. For stress perfusion studies, a vasodilator may be administered as well. Patients feel warmth briefly during injection. Any unusual sensation is reported immediately.
4. Entering the Scanner
The table advances into the bore. I maintain audio contact throughout. A call button remains in hand. For claustrophobic patients, I use stepwise reassurance and coaching. A support person may wait nearby if the facility allows. Breathing remains normal unless instructed otherwise.
5. Breath-Holding Instructions
Breath holds are short. Typically 8 to 15 seconds. I cue each hold and release. Stable breath holds reduce motion artefacts, especially on cine, perfusion, and mapping sequences. If a patient struggles, we adjust sequence timing or use free-breathing techniques with motion correction.
6. Image Acquisition Phase
The protocol proceeds in blocks. Localisers, cine images, then perfusion or mapping as indicated. I adapt sequences to the clinical question. High heart rates, arrhythmias, or device artefacts may require modified approaches. The result is a tailored set of images that answer defined questions.
Post-Scan Recovery Steps
Once the heart MRI scan finishes, I remove lines and leads and confirm that the patient feels well. Any contrast-related symptoms are reviewed. I outline when to resume normal activities. The images then undergo structured analysis and are reported to the referring clinician. A short debrief on expected timelines helps reduce anxiety.
Understanding Heart MRI Benefits and Safety
List of Key Advantages
-
Excellent soft tissue contrast for myocardium, valves, and pericardium.
-
Quantitative data for flow, volumes, and function.
-
Whole-heart coverage without ionising radiation.
-
Reliable assessment of scar and viability that informs therapy.
-
Useful when echocardiography windows are limited.
Radiation-Free Imaging Benefits
A heart MRI scan uses magnetic fields and radiofrequency, not X-rays. This allows repeated assessments for chronic conditions without cumulative radiation. It also enables comprehensive evaluation in younger patients who will require long follow up. For surveillance after interventions, this becomes practical and safe.
Metal Implant Considerations
MRI safety depends on device type and its specific MRI rating. I verify whether an implant is MR-unsafe, MR-conditional, or MR-safe. Pacemakers and defibrillators increasingly have MRI-conditional labelling, which permits scanning under defined parameters. When in doubt, I consult the implant card and the device manual, and coordinate with cardiology for pre-scan checks and post-scan reprogramming where required.
Contrast Dye Safety Information
Gadolinium-based agents help identify scar and inflammation. I screen kidney function, prior reactions, and pregnancy status before use. Hydration and supervision reduce rare risks. For severe renal impairment, I weigh risks and benefits carefully and may proceed only if essential and safe alternatives are unavailable. Non-contrast protocols remain valuable for function and anatomy when contrast is unsuitable.
Claustrophobia Management Options
Anxiety can derail good imaging. I offer a structured plan: an upfront explanation, practice breath holds, and continuous communication. Wide-bore scanners and calming audio reduce distress. Open systems or light sedation are considered for severe claustrophobia. A simple breathing routine often helps. In short, a plan is better than reassurance alone.
Cardiac MRI Cost and Availability in India
Price Range Across Major Cities
Pricing varies by city and facility tier. Night or off-peak appointments may reduce cost. For context, listings show starting prices near DoctorC at Rs 9,500 in Mumbai. One Delhi provider advertises approximately Rs 9,499 for a study with contrast as HOD notes. These figures are indicative and subject to change.
Factors Affecting MRI Cost
-
Protocol complexity: stress perfusion and advanced mapping increase time and cost.
-
Contrast use: agents, injectors, and monitoring add fees.
-
Equipment class: newer wide-bore or higher field scanners command a premium.
-
Radiologist expertise: subspecialty reporting may increase pricing.
-
Hospital vs diagnostic centre: larger hospitals usually cost more.
-
Follow up and add-on sequences: additional views can raise the final amount.
Insurance Coverage Guidelines
Coverage depends on policy terms and the clinical indication. When a heart MRI scan is requested to guide management, many insurers consider it medically necessary. I advise obtaining a pre-authorisation with the referral letter and clinical notes. Documenting failure or limitations of other modalities strengthens approval.
Finding Quality MRI Centres
I look for three signals. Experienced cardiac radiographers, consistent reporting standards, and access to multidisciplinary input if needed. High-quality centres publish their protocols and offer post-report discussion. If a referring team has a regular partner centre, outcomes tend to be smoother. Reputation matters, but consistent technique matters more.
Making Informed Decisions About Heart MRI
The decision to book a heart MRI scan should be deliberate. I start with the clinical question: what must this test change in management. If the answer is specific and actionable, the scan is warranted. If the answer is vague, I refine the indication or consider alternatives. A clear question produces a clear protocol and a clear report.
There is also timing. A heart MRI scan early in the pathway can prevent redundant tests and delays. But choices still depend on access and urgency. When valves or perfusion need precise quantification, it often earns its place as the definitive step. When an echo already answers the question, I reserve MRI for follow up or complexity.
Finally, preparation influences result quality. Good breath holds, stable heart rate, and complete safety screening help more than new software. Precision in, precision out. That is the core principle.
Reference Summary and Practical Aids
|
Item |
What to remember |
|---|---|
|
Primary use |
Quantify function, flow, and scar to guide decisions. |
|
Preparation |
No metal, check devices, avoid caffeine if stress is planned. |
|
During scan |
Short breath holds. Clear instructions. Call button in hand. |
|
Contrast |
Screen kidneys and prior reactions. Use only if clinically useful. |
|
When to choose MRI |
When echo leaves gaps, when tissue characterisation will change management. |
Quick Decision Checklist
-
Define the clinical question the heart MRI scan must answer.
-
Confirm safety: devices, renal function, and prior contrast reactions.
-
Select protocol: function only, perfusion, mapping, or full viability study.
-
Prepare the patient: expectations, breath holds, and anxiety plan.
-
Plan follow up: ensure results feed directly into management.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a cardiac MRI scan typically take?
Most studies take 30 to 60 minutes. Add 15 minutes if stress perfusion is required. Complex congenital evaluations may take longer. I advise planning for about 90 minutes in the department to include preparation and recovery.
Can I eat before a heart MRI scan?
Light meals are generally acceptable. For stress studies, I ask patients to avoid caffeine for 12 to 24 hours because it can blunt vasodilator effects. Heavy meals immediately before scanning are unhelpful for breath holds. Water is fine unless instructed otherwise.
Is cardiac MRI better than echocardiogram?
Each tool has strengths. Echocardiography is fast, accessible, and excellent for valves and bedside assessment. A heart MRI scan offers superior tissue characterisation and precise quantification of volumes, flows, and scar. I choose based on the clinical question. It is not a contest, it is a sequence.
Who should avoid getting a heart MRI scan?
Patients with MR-unsafe implants or fragments should not enter the scanner. Those with severe renal impairment may not be candidates for gadolinium contrast. Unstable patients who cannot lie flat or follow breath holds may require stabilisation or an alternative test first.
What is the difference between cardiac MRI with and without contrast?
Non-contrast sequences provide anatomy and function. Contrast sequences highlight scar, inflammation, and perfusion. If I need to judge viability or detect myocarditis, I use contrast. If the question is basic function or volumes, non-contrast may suffice. Both approaches can be combined in one heart MRI scan.
How soon will I receive my heart MRI results?
Reporting schedules vary by centre. Many results are available within one to three working days. Urgent findings are escalated on the same day. I encourage patients to arrange a follow up appointment for a structured discussion rather than waiting for a phone summary.







 We do what's right for you...
We do what's right for you...








